What Do Window Ratings Mean? A Guide to Understanding Energy Efficiency

Windows are more than just a view to the world; they play a critical role in the energy efficiency of a home. With the rising emphasis on sustainable living and reducing energy consumption, understanding window ratings has become increasingly important. Let’s look at common window ratings and what they mean for your home’s energy efficiency.
How Are Windows Rated?
The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) administers a voluntary initiative that evaluates, certifies, and marks windows, doors, and skylights according to their energy efficiency assessments. The labeling by NFRC offers a trustworthy method to assess the energy attributes of windows and facilitates product comparisons.
The label issued by NFRC is present on all window, door, and skylight items that qualify for ENERGY STAR recognition. Think of it like car shopping — the same way you’d read the sticker on the car window, you’ll want to read the sticker on windows for your home.
Next, we’ll explain what the information on that sticker tells you.
5 Common Window Ratings
Windows are rated based on several key factors that contribute to their energy efficiency, overall performance, and longevity. Here are the main factors that contribute to window ratings (you’ll see them represented on ENERGY STAR-certified window stickers.
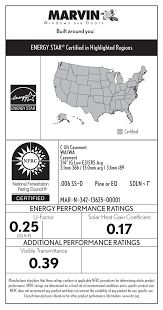
1. U-Factor
A window’s U-factor measures its ability to keep heat from escaping your home. It takes into account the frame, glass, and spacer materials. The lower the U-factor, the better the heat retention. A rating of 0.25 or lower is considered good, while a 1.20 or higher is considered poor.
2. Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
A window’s solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) rates how well it can block sunlight-generated heat. Ratings range from 0 to 1 — the lower the number, the better the window is at blocking heat. A rating of 0.25 or lower is considered good, while a 0.80 or higher is considered poor.
3. Visible Transmittance
A window’s visible transmittance (VT) measures how much light passes through a window. While it doesn’t directly impact energy efficiency, it affects the need for artificial lighting during the day. Ratings range from 0 to 1, with a higher rating indicating more light is allowed through the window. A rating of 0.70 or higher is considered good, while a 0.40 or lower is considered poor.
4. Air Leakage
A window’s air leakage rating measures how much air passes through its frame. The rating is given in cubic feet per minute per square foot of window area, with lower numbers indicating less air leakage. A rating of 0.3 or lower is considered good, while a 0.5 or higher is considered poor.
5. Condensation Resistance
A condensation resistance rating isn’t always included, but it measures how well a window resists condensation forming on the inside surface. Ratings range from 0 to 100, with higher numbers indicating better resistance to condensation. A rating of 50 or higher is considered good, while a 10 or lower is considered poor.
The Benefits of Good Ratings
Choosing windows with good ratings can bring several benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: Windows with good U-factor and SHGC ratings help regulate indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This leads to lower energy consumption (and bills!).
- Comfort: Well-insulated windows keep your home more comfortable year-round by minimizing drafts and temperature fluctuations.
- Natural Light: Windows with higher VT ratings allow ample natural light to enter your space, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. Hello, vitamin D!
- Condensation Management: Higher condensation resistance ratings help prevent moisture-related issues in your home. This means healthier air quality.
Certification Labels
While you’re window shopping, you’ll also notice various certification labels. They’re just as important to understand as window ratings, as they’ll give you information about their manufacturing and performance quality.
NFRC Certification
The NFRC assists consumers in comparing window functionality through diverse metrics such as U-factor, SHGC, air leakage, VT, and condensation resistance. The NFRC labeling encompasses multiple test standards, including NFRC 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500.
ENERGY STAR Certification
The ENERGY STAR certification label is determined by evaluating U-factor and SHGC ratings. The certification itself doesn’t encompass a direct assessment. Instead, it utilizes the comprehensive window thermal test results from NFRC to establish geographic zones across the country. For each zone, specific U-factor and SHGC values are recommended.
NAMI Structural Certification
The National Accreditation and Management Institute (NAMI), an independent entity, conducts inspections and certifies windows, doors, and other products. It assigns energy performance ratings grounded in metrics like U-factor and SHGC. A NAMI certification label indicates the testing standard, displaying the manufacturing facility’s name, achieved grade or performance level, product series or model name, and other pertinent details.
AAMA Certification
The American Architectural Manufacturers Association (AAMA) certification entails a trio of assessments: water leakage, structural strength, and air leakage. Products exclusively evaluated for thermal performance receive a Silver Certification label. Conversely, products examined for structural, air, and water performance alongside thermal performance garner a gold label.
Where to Find Energy-Efficient Windows
When looking for energy-efficient windows, consider reputable brands like:
- Andersen™ Windows & Doors
- JELD-WEN® Windows & Doors
- Marvin®
- North Star Windows & Doors
- Silver Line® Windows & Doors
These brands offer a range of window options with varying ratings to match your specific needs. They are known for their craftsmanship, trusted for their great service and warranty options, and are available here at Standard Lumber & Supply.
Contact our team to learn more about our energy-efficient window options and how we can support your home project.

